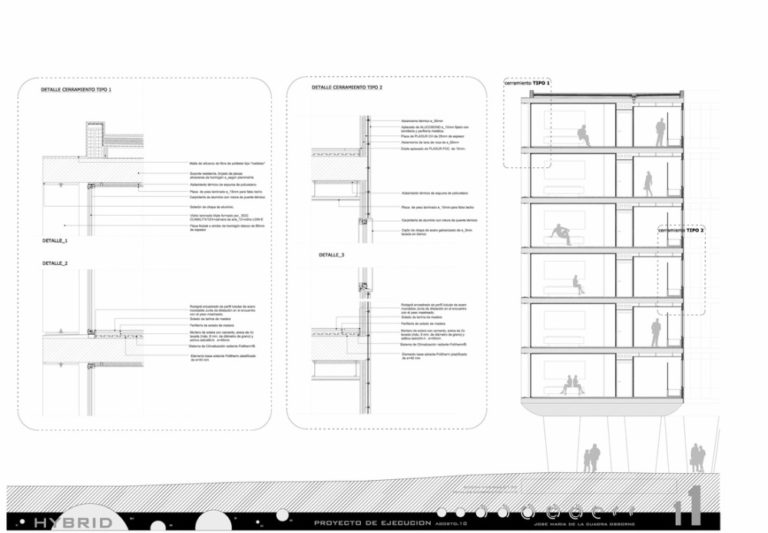
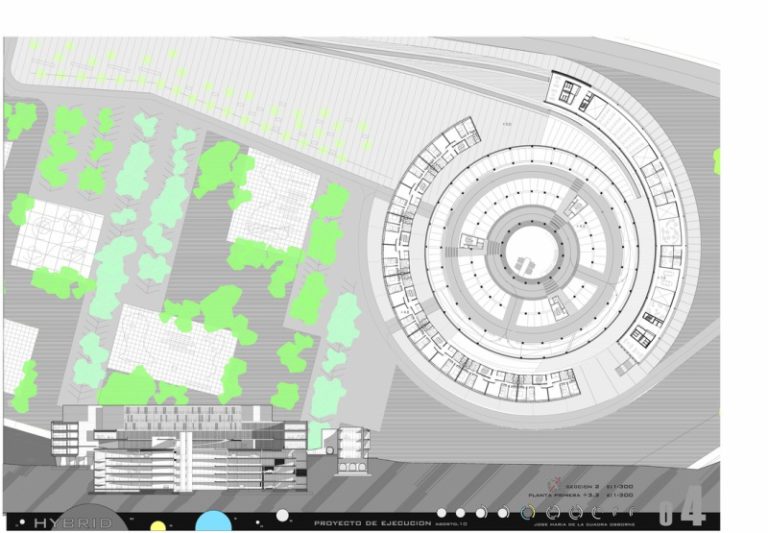
Status
Use
Location
Client
Budget
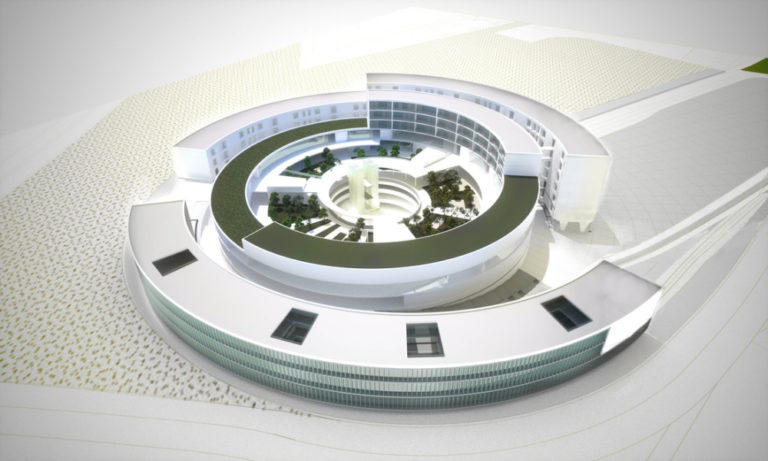
La arquitectura híbrida es un enfoque que combina diferentes técnicas, materiales, estilos o metodologías para crear estructuras innovadoras y adaptables. A menudo, este término se utiliza para describir proyectos arquitectónicos que combinan la construcción tradicional con tecnología avanzada, integrando conceptos de sostenibilidad, eficiencia energética y diseño funcional. La arquitectura híbrida puede aplicarse en varios contextos:
Características Clave de la Arquitectura Híbrida
Combinación de Materiales: La arquitectura híbrida se caracteriza por el uso de materiales contrastantes, como concreto y madera, acero y vidrio, o técnicas constructivas tradicionales junto con componentes prefabricados y modulares. Esta combinación permite aprovechar las mejores propiedades de cada material para crear espacios únicos.
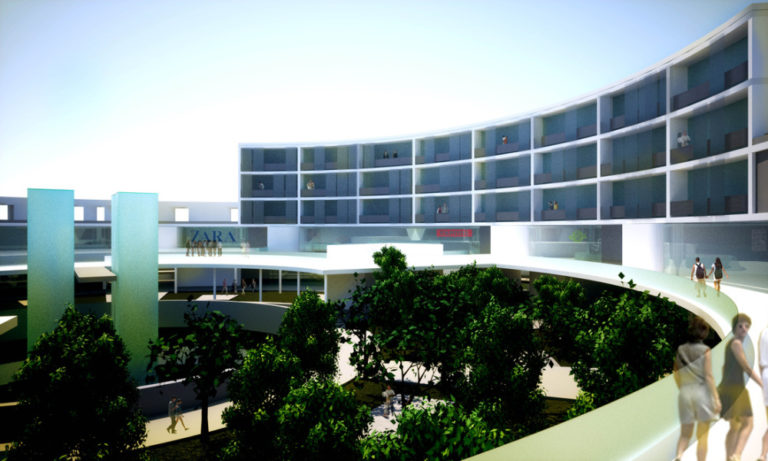
Flexibilidad Funcional y Adaptabilidad: Este tipo de arquitectura busca crear espacios que se adapten a múltiples usos y necesidades, respondiendo a los cambios en el entorno o en las necesidades del usuario. Por ejemplo, edificios con muros móviles, techos retráctiles o espacios que pueden transformarse fácilmente en función de su uso.
Integración Tecnológica: Los proyectos híbridos suelen incorporar tecnología avanzada, como sistemas de automatización, energías renovables o infraestructura digital. Esto incluye la integración de sensores, sistemas domóticos, paneles solares y otras soluciones tecnológicas que hacen a los edificios más inteligentes y eficientes.
Diseño Sostenible y Ecológico: La arquitectura híbrida tiene una fuerte orientación hacia la sostenibilidad. Esto se manifiesta en el uso de materiales reciclables, estrategias de construcción pasiva para reducir el consumo energético y diseños que minimizan el impacto ambiental. En muchos casos, se utilizan elementos naturales, como jardines verticales y cubiertas vegetales, para mejorar la calidad ambiental del edificio.
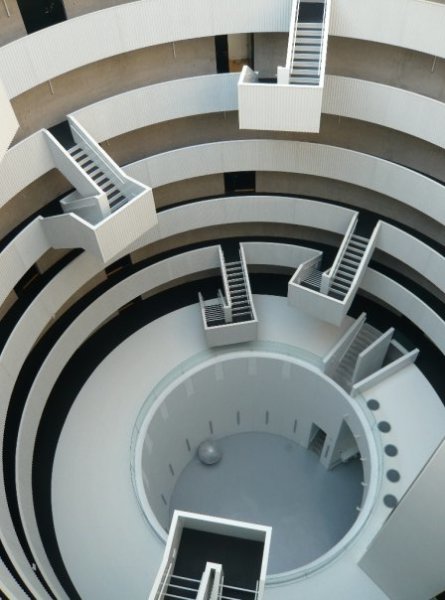
Estética Contemporánea y Vanguardista: La estética en la arquitectura híbrida tiende a ser contemporánea y audaz, con formas geométricas, espacios abiertos y estructuras que desafían los límites tradicionales de la arquitectura.
Hybrid architecture is an approach that combines different techniques, materials, styles, or methodologies to create innovative and adaptable structures. This term is often used to describe architectural projects that blend traditional construction with advanced technology, integrating concepts of sustainability, energy efficiency, and functional design. Hybrid architecture can be applied in various contexts:
Key Characteristics of Hybrid Architecture
Combination of Materials: Hybrid architecture is characterized by the use of contrasting materials, such as concrete and wood, steel and glass, or traditional construction techniques alongside prefabricated and modular components. This combination allows the design to leverage the best properties of each material to create unique spaces.
Functional Flexibility and Adaptability: This type of architecture aims to create spaces that adapt to multiple uses and needs, responding to changes in the environment or user requirements. For instance, buildings with movable walls, retractable roofs, or spaces that can easily transform depending on their use.
Technological Integration: Hybrid projects often incorporate advanced technology, such as automation systems, renewable energy sources, or digital infrastructure. This includes the integration of sensors, smart home systems, solar panels, and other technological solutions that make buildings smarter and more efficient.
Sustainable and Eco-friendly Design: Hybrid architecture has a strong focus on sustainability. This is reflected in the use of recyclable materials, passive construction strategies to reduce energy consumption, and designs that minimize environmental impact. In many cases, natural elements such as vertical gardens and green roofs are used to enhance the environmental quality of the building.
Contemporary and Avant-garde Aesthetics: The aesthetics of hybrid architecture tend to be contemporary and bold, with geometric forms, open spaces, and structures that challenge traditional architectural boundaries.